Integrating Chainlink Price Feeds: A Practical Guide
Decentralized price feeds from Chainlink offer an alternative to centralized APIs. Here’s a complete integration guide from setup to deployment.

While centralized APIs like CoinGecko or CoinMarketCap are simple and free, displaying live cryptocurrency prices from a decentralized source is possible and has many advantages. Chainlink Price Feeds offers decentralized, tamper-proof price data which is maintained by oracle networks.
This guide walks through the complete integration process, from setup to deployment. The final implementation from this guide is live at web3fuel.io/tools/crypto-prices.
// TL;DR – Quick Implementation Guide
To integrate Chainlink Price Feeds into your own project:
- Install
web3.pyviapip install web3 - Find price feed addresses at data.chain.link
- Obtain a free RPC endpoint from Alchemy
- Use the code examples below as starting points
- Deploy and iterate based on requirements
Start with a simple implementation (one price feed, basic display), then add features based on needs.
Table of Contents ▼
// What Are Chainlink Price Feeds?
Before we dive into the code, let’s talk about what Chainlink actually is and why it matters.
Chainlink is a Decentralized Oracle Network (DON), which offers a solution to bring off-chain data onto the blockchain. Since smart contracts can’t access external data on their own (for example, they can’t make API calls to CoinGecko or check the weather), oracle networks, like Chainlink, act as a bridge between on-chain and off-chain worlds.
Here’s how it works: Independent oracle nodes monitor various data sources and aggregate the information. Once the nodes reach consensus on a datapoint, they transmit it to the blockchain. This decentralized approach means there’s no single point of failure; if one node goes down or provides bad data, the system keeps running.
Chainlink has facilitated over $15 trillion in transaction value across DeFi, making it the most widely used oracle network in crypto. Many major DeFi protocols, such as Aave, Synthetix, Compound etc. rely on Chainlink for price data.
Why Price Feeds Matter
Chainlink offers several products (VRF for randomness, Automation for keeper functions, CCIP for cross-chain messaging), but Price Feeds are the most widely used. They provide real-time price data for crypto assets by aggregating prices from multiple premium sources like CoinGecko, CoinMarketCap, and major exchanges.
Each price feed is a smart contract on Ethereum (and other chains) that gets updated regularly by the oracle network. Anyone can read from these contracts for free without any API keys or rate limits. Just open data on the blockchain.
// Building the Integration
Now for the implementation. The goal for this tutorial is create a dashboard that displays live prices for major cryptocurrencies (BTC, ETH, LINK, AVAX, MATIC) using Chainlink’s oracle network. You will easily be able to add any other live cryptocurrency prices during this setup.
Step 1: Setting Up Web3.py
To interact with Ethereum smart contracts from a Flask backend, install Python’s web3.py library which is the standard tool for blockchain interactions.
Add it to your requirements.txt file:
Then install it with pip install web3 and you’re ready to start talking to Ethereum.
Step 2: Connecting to Price Feed Contracts
Each Chainlink Price Feed is a deployed smart contract on Ethereum mainnet. All available price feed addresses can be found at data.chain.link.
For this implementation, the five major pairs we used are:
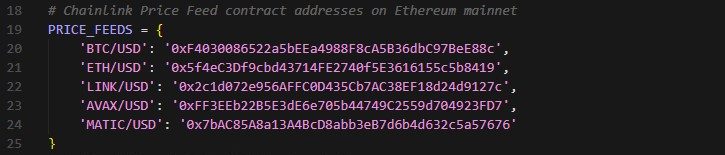
Implement a fallback system so if one RPC fails, the code automatically tries the next one. This pattern is covered in detail in the “Challenges” section below.
Step 3: Fetching Prices
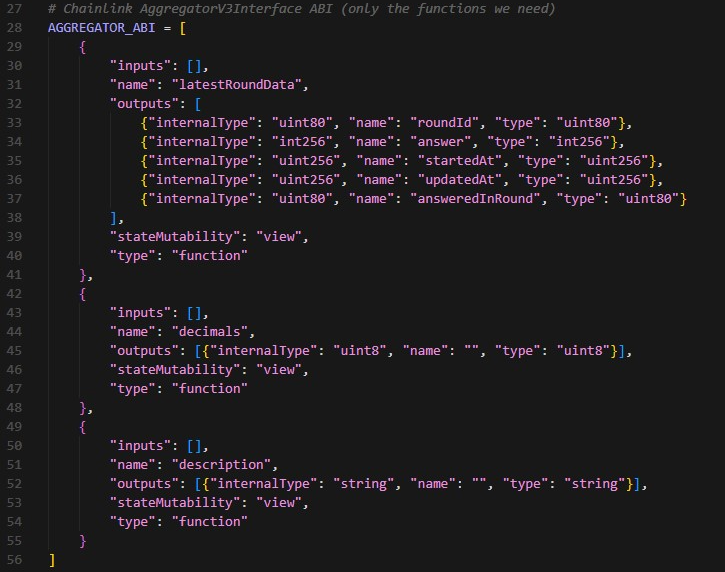
The core functionality involves reading price data from Chainlink contracts. Every Chainlink Price Feed implements the AggregatorV3Interface, which provides two essential functions:
latestRoundData()– Returns the most recent price.decimals()– Returns how many decimal places the price uses.
Here’s the minimal ABI (Application Binary Interface) we need:
Then create a function to fetch the price from a specific feed:
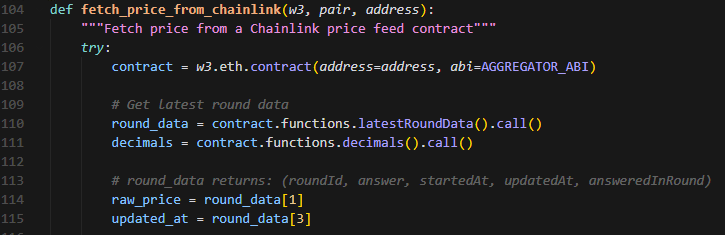
The latestRoundData() function returns five values:
- roundId: The round ID of this price update
- answer: The actual price (as a raw integer)
- startedAt: When the round started
- updatedAt: When the price was last updated on-chain
- answeredInRound: The round ID when the answer was computed
We only really care about answer (the price) and updatedAt (the timestamp).
Step 4: Handling Decimals
Blockchains don’t handle floating-point numbers well, so Chainlink stores prices as large integers. For example, Bitcoin trading at $92,345.94 is stored as 9234594000000.
Convert this to a readable price by dividing by the appropriate decimal places, which the decimals() function provides:
All USD price pairs use 8 decimals, so for example, the math looks like this:
raw_price = 9234594000000 (from BTC/USD feed)
decimals = 8
price = 9234594000000 / 100000000 = $92,345.94
Important: Always call decimals() from the contract rather than hardcoding it. While all USD pairs currently use 8 decimals, this could change for future feeds or different asset types.
Step 5: Building the Frontend
With the backend functional, implement a card-based layout where each cryptocurrency displays:
- Token symbol and icon
- Current price
- Price change indicator (up/down arrows)
- On-chain update timestamp
- Links to Chainlink data and Etherscan
First, define the token metadata:
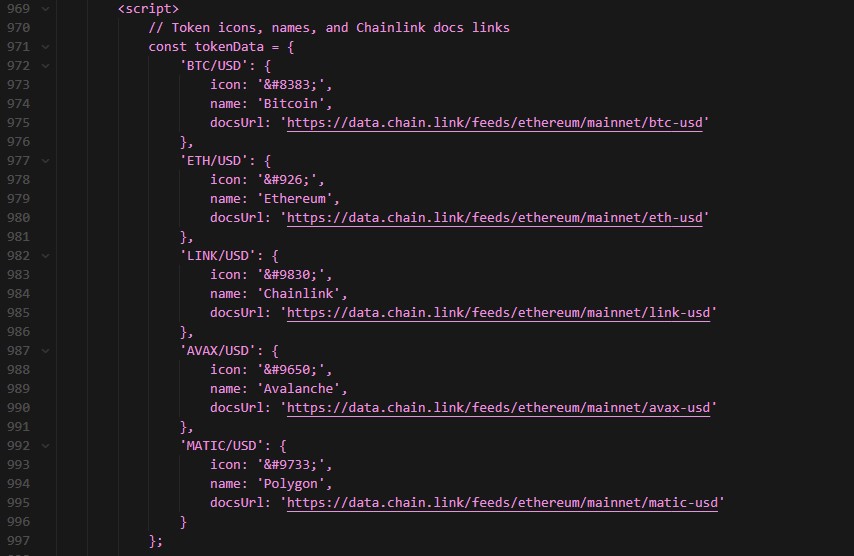
Then create a function to generate the HTML for each price card:
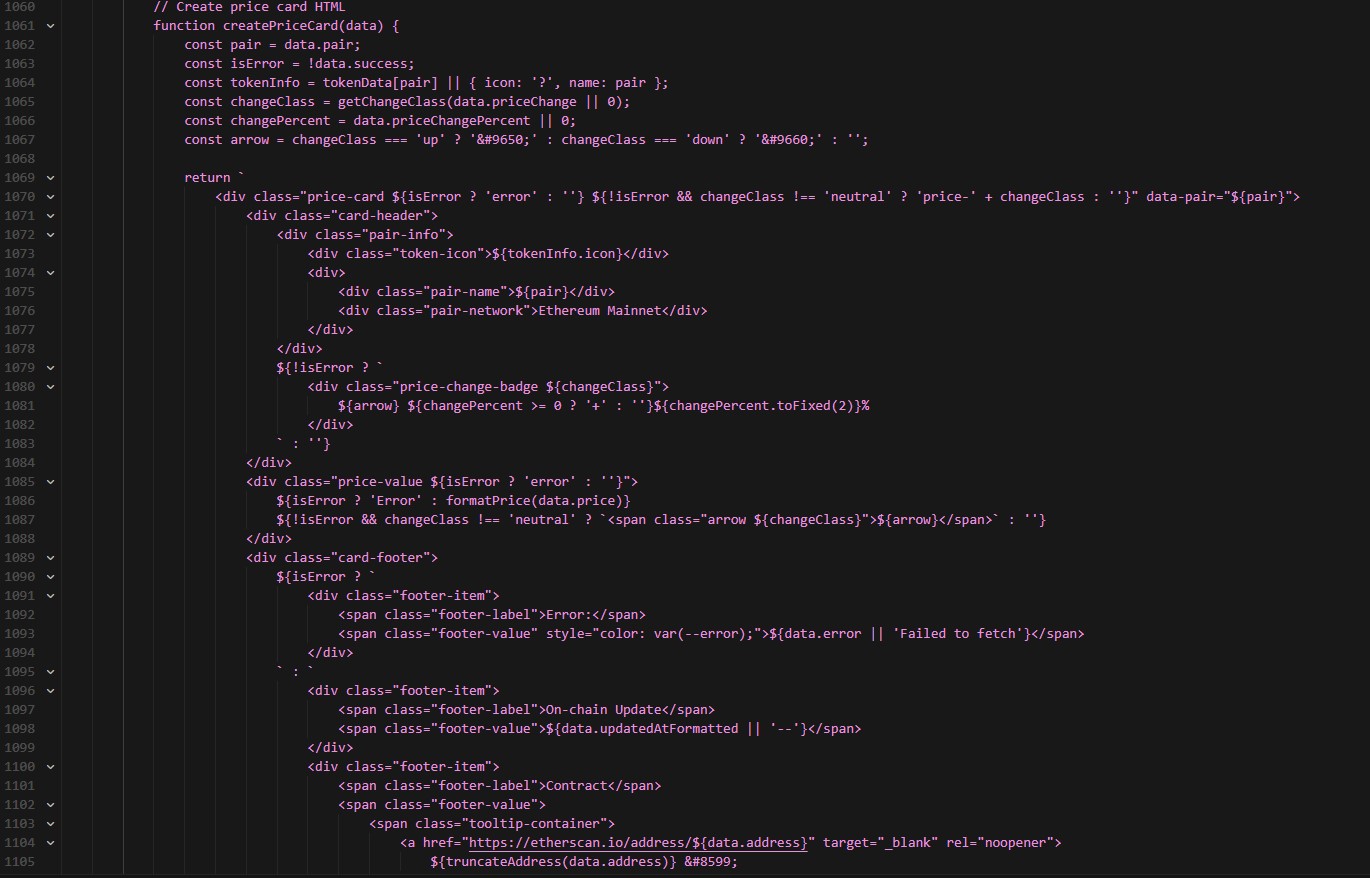
Add proper price formatting so large numbers like Bitcoin display with commas while smaller numbers like MATIC show more decimal places.
Step 6: Adding Auto-Refresh
Implement automatic updates by setting up a 30-second refresh interval with a visible countdown:
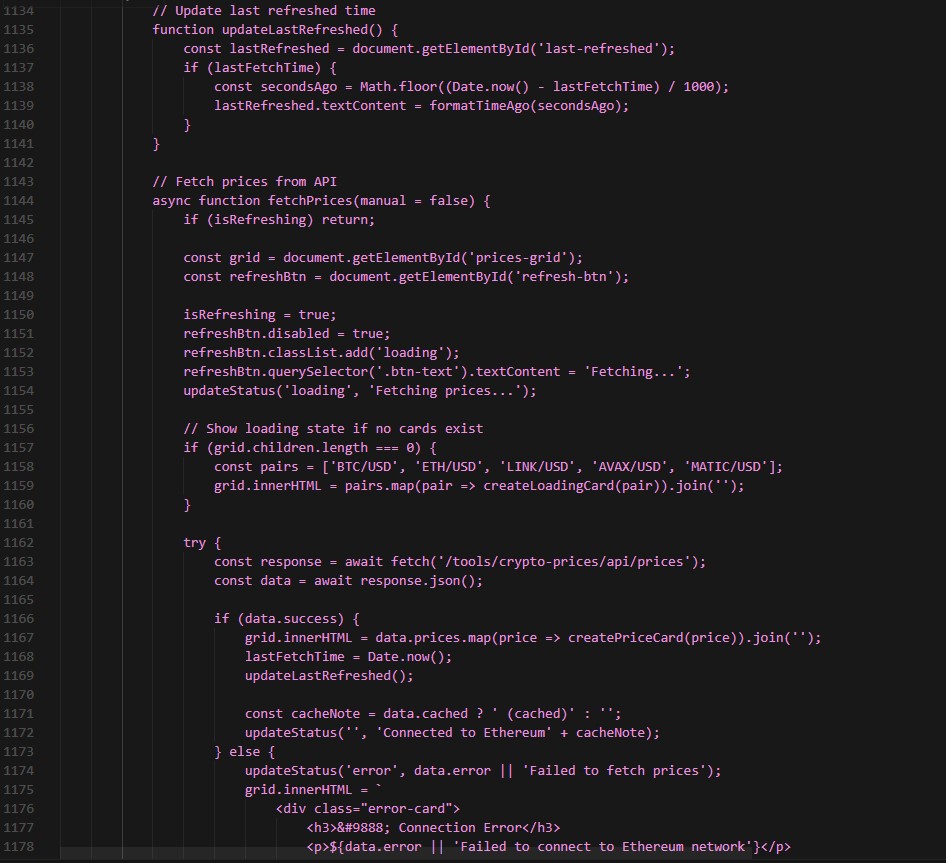
Users can also click “Refresh Now” to fetch prices immediately, which resets the countdown timer.
That’s it! The crypto price fetching dashboard is now complete.
// Challenges and Solutions
Several technical challenges emerged during our implementation. Here’s how we addressed them.
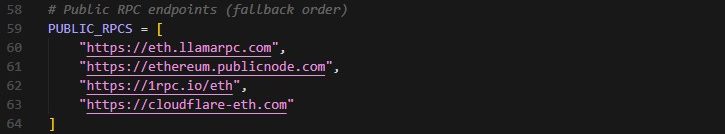
Challenge 1: RPC Rate Limits
Problem: Public RPC endpoints like Cloudflare and 1RPC impose rate limits. During testing, connection timeouts and “too many requests” errors are common.
Solution: Implement a fallback system that tries multiple RPC providers in sequence:
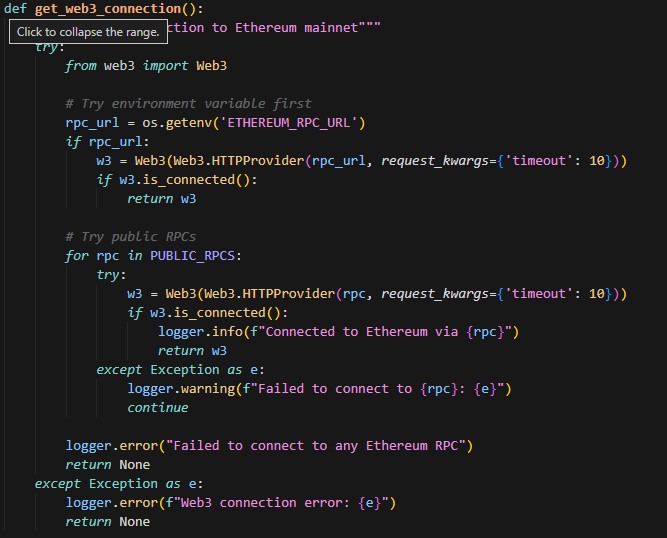
If the primary RPC (Alchemy) becomes unavailable, the code automatically falls back to public endpoints. For production deployments, use Alchemy or Infura since both offer free tiers with reasonable usage limits and significantly better reliability.
Challenge 2: Decimal Conversion Errors
Problem: Hardcoding decimals = 8 in price conversion works initially, but fails when testing with different assets, producing incorrect prices due to varying precision across feeds.
Solution: Always fetch decimals dynamically from the contract:
While all USD pairs currently use 8 decimals, this could change for future feeds or non-USD pairs. Always call decimals() rather than hardcoding values for safer, more maintainable code.
Challenge 3: Handling Stale Data
Problem: Users refreshing the page rapidly hammer the RPC endpoint, potentially hitting rate limits. Additionally, displaying when prices were last updated helps users assess data freshness.
Solution: Implement a 30-second server-side cache with thread-safe locking:
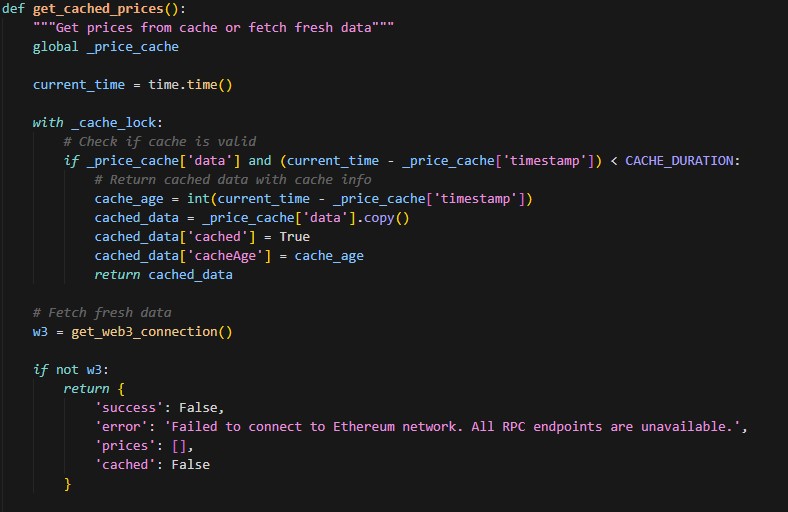
The API response includes cached: true/false and cacheAge so the frontend can indicate whether it’s displaying cached data. This approach dramatically reduces RPC calls and improves application reliability.
// Key Takeaways
Several important lessons emerged from this integration:
- Chainlink price feeds are reliable, but not instant: Prices update roughly every 0.5-2% deviation or hourly (whichever comes first). This latency works fine for dashboards and data displays, but trading platforms or DEXs require different solutions.
- Free RPC endpoints have limitations: Public RPCs work for testing and small projects, but suffer from unreliability and rate limits. For production applications, investing 10 minutes to obtain a free Alchemy or Infura key provides significantly better results.
- Error handling is critical: Calling external contracts over RPC endpoints introduces multiple failure points. Networks may go down, contracts experience congestion, RPCs hit rate limits. Build in fallbacks, retries, and clear error messages for users.
- Decimal precision matters: Blockchain math requires exact precision. Always verify decimal handling because a single misplaced zero can turn $50,000 into $0.50.
- Caching improves stability: Without server-side caching, RPC calls face constant throttling. A simple 30-second cache makes applications more stable and faster.
// Potential Extensions
This implementation serves as a foundation for additional features:
- Multi-chain support: Expand price feeds to Arbitrum, Base, and Polygon.
- More assets: Include additional major DeFi tokens beyond the current five.
- Historical charts: Leverage Chainlink’s historical data for price trend visualization.
- Price alerts: Enable user-defined notifications for price thresholds.
- CCIP integration: Explore Chainlink’s cross-chain messaging protocol for advanced features.
// The Final Implementation
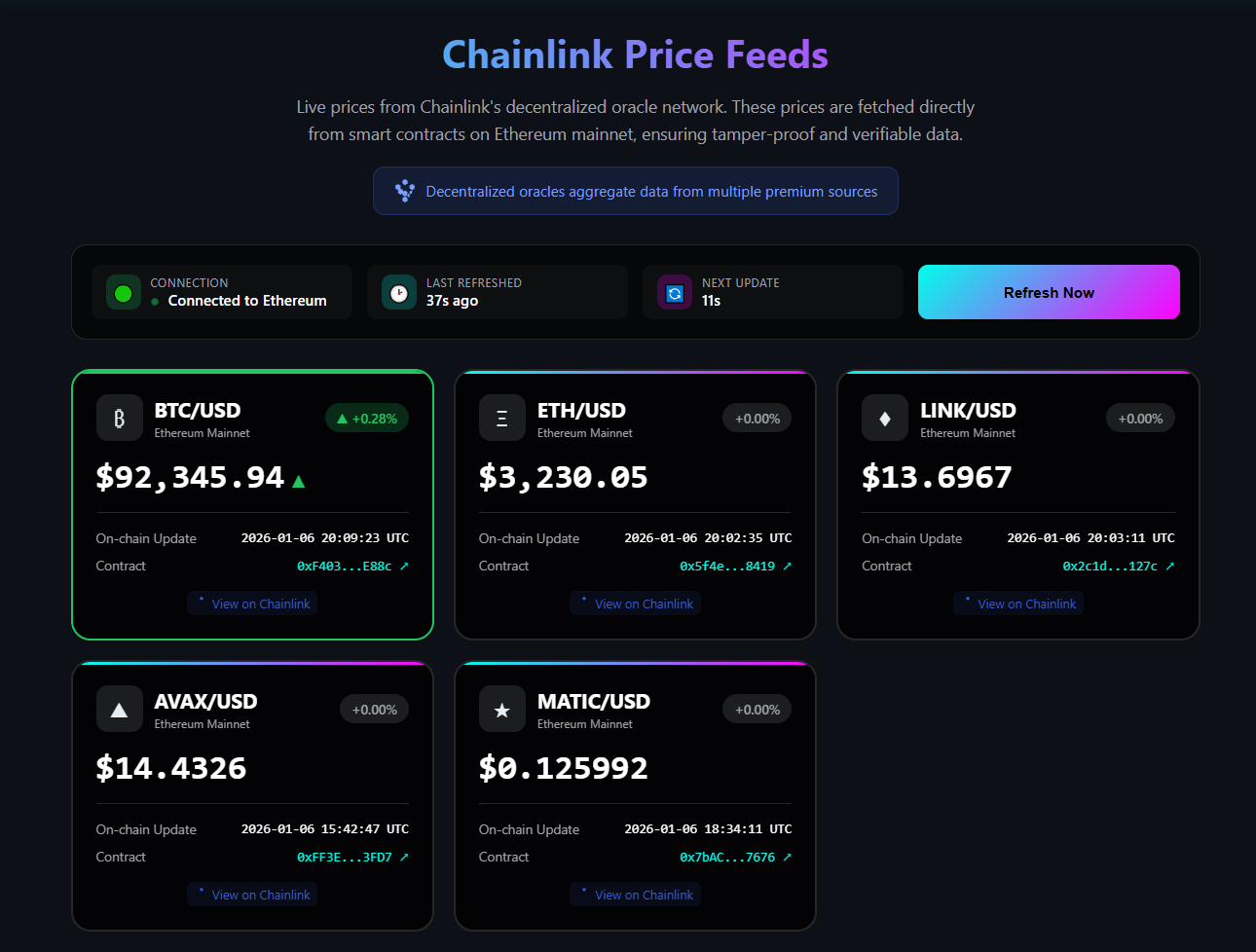
The complete dashboard is available at web3fuel.io/tools/crypto-prices. It displays real-time prices from Chainlink’s decentralized oracle network, updates every 30 seconds, and shows price change indicators with clear directional arrows.
This implementation demonstrates hands-on experience integrating production oracle infrastructure and is valuable knowledge for developer relations and technical communication roles.
Here’s a screenshot of what the dashboard looks like live:
// Resources
- Contract addresses and documentation: docs.chain.link/data-feeds
- Full code available at: https://github.com/zzzandy-eth/web3fuel
Alex G.
Cross-Chain Infrastructure Analyst | Protocol Security Researcher
Building insights for the multi-chain world at Web3Fuel.io. Focused on cross-chain bridge security, protocol analysis, and helping users navigate infrastructure safely.
Documenting the journey from DeFi user to protocol analyst, one bridge at a time.
